Global Voltage Standards and Transformer Adaptation 11kv
I. Introduction
Electric power system voltage standards are not uniform worldwide. Different countries have established varying voltage and frequency standards based on their power infrastructure, historical development, and technical requirements. As a crucial component of power transmission and distribution, transformers must be adjusted according to different national standards to ensure efficient and safe electricity transmission. This article will explore global voltage standards, transformer design and applications, and transformer adaptability in the international market.

II. Global Voltage Standards
1. Voltage Classification
The world’s power grid voltages are mainly classified as follows:
- Low Voltage (LV): 100V – 240V
- Medium Voltage (MV): 1kV – 69kV
- High Voltage (HV): 69kV and above
2. Voltage and Frequency Standards by Country
| Country/Region | Rated Voltage (V) | Frequency (Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| USA, Canada, Mexico | 120/240 | 60 |
| EU (Most Countries) | 230 | 50 |
| UK | 230/400 | 50 |
| Japan | 100 | 50 (East) / 60 (West) |
| China | 220/380 | 50 |
| Australia | 230/400 | 50 |
| Russia | 220/380 | 50 |
| India | 230/400 | 50 |
| Saudi Arabia | 127/220/400 | 60 |
| Brazil | 127/220 | 60 |
It is evident that global power grid standards are mainly divided into two frequency groups: 50Hz and 60Hz, with 50Hz being the dominant standard.
III. Role and Classification of Transformers
1. Basic Functions of Transformers
Transformers are essential in power transmission and distribution, serving the following functions:
- Voltage Transformation: Step-up or step-down to adapt to different voltage standards.
- Energy Transmission: Reduce line losses and improve efficiency.
- Power Isolation: Enhance safety and prevent short circuits and electric shocks.
- Voltage Regulation: Manage load fluctuations and ensure stable power supply.
2. Classification of Transformers
By Application:
- Step-up Transformer
- Step-down Transformer
- Distribution Transformer
- Power Transformer
- Isolation Transformer
By Cooling Method:
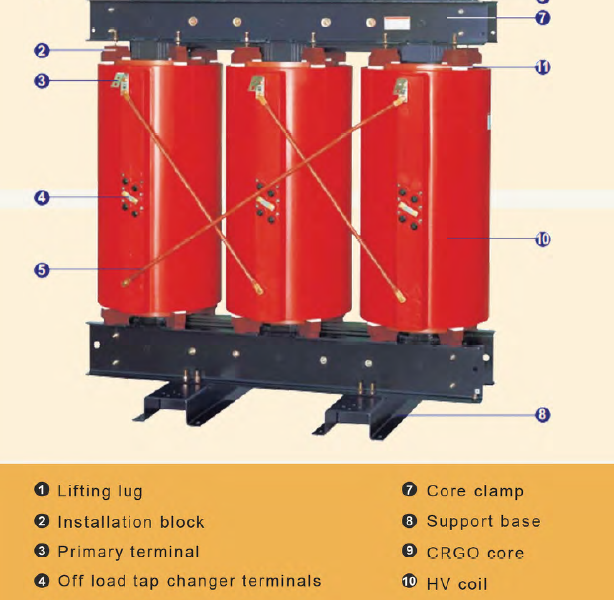
- Oil-immersed Transformer
- Dry-type Transformer
By Structure:
- Single-phase Transformer
- Three-phase Transformer
IV. Transformer Demand in Different Markets

1. North American Market (120V/240V, 60Hz)
- Predominantly uses single-phase transformers for residential and commercial supply.
- Industrial applications use three-phase 208V, 480V, and higher voltages.
- High-efficiency transformers required to meet DOE standards.
2. European Market (230V/400V, 50Hz)
- Primarily a three-phase power grid, with industrial equipment using 400V.
- Renewable energy market (wind and solar power) drives demand for specialized transformers.
- Transformers must comply with IEC 60076 standards.
3. Asian Market (220V/380V, 50Hz)
- China, India, and other countries have high power demand, driving HV transformer needs.
- Manufacturing standards align with GB/T 6451-2015.
4. Middle Eastern Market (127/220V & 400V, 60Hz)
- Primarily three-phase power supply, serving the oil and gas industry.
- Transformers must withstand high temperatures and sandstorms, adhering to ANSI and IEC standards.
V. Key Technologies for Transformer Adaptation to Global Voltage Standards
1. Voltage Adaptation
- Multi-tap Transformers allow compatibility with various voltage standards.
- Autotransformers provide multiple output voltages.
2. Frequency Adaptation
- 50Hz transformers can operate on 60Hz networks but require derating.
- 60Hz transformers used on 50Hz networks may overheat.
3. Insulation and Weather Resistance
- Outdoor transformers need protection against moisture, dust, and UV exposure.
- Special-purpose transformers (e.g., offshore wind power) must resist salt spray corrosion.
VI. Future Trends and Developments
1. Smart Transformers
- IoT-enabled remote monitoring
- Digital management for improved efficiency
2. Renewable Energy Transformers
- Designed for photovoltaic and wind power stations
- Must have a wide input range and high conversion efficiency
3. Superconducting Transformers
- Utilize high-temperature superconducting materials to reduce energy loss.
- Potential applications in efficient transmission and grid stability.
VII. Conclusion
Different voltage and frequency standards worldwide dictate transformer specifications and design. With energy transitions, smart grid advancements, and the increasing use of renewable energy, transformer technology continues to evolve. For manufacturers, understanding various national grid standards, optimizing transformer design, and complying with global regulations are key to competing in the international market.
Transformers are not only the core of power grids but also an essential part of future energy development.
